Ginseng
Ginseng
Renshen
人參
Source
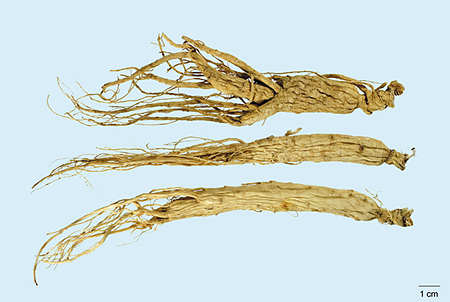
The root of Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (Fam. Araliaceae).
Distribution
Mainly in Chinese provinces such as Jilin, Liaoning and Heilongjiang. Mostly cultivated.
Harvest & Processing
Collect cultivated ginseng in autumn; wash clean; remove branch roots; dry ginseng under the sun or by heat to produce ' Shengshai shen' (Sun-Dried Fresh Ginseng), or dry ginseng under the sun without removing branch roots to produce ' Quanxu Shengshai shen' (Sun-Dried Whole Fresh Ginseng).
Description
Axial root of Sun-Dried Fresh Ginseng spindle-shaped or cylindrical; outer surface greyish-yellow; upper part or entire root marked with sparse, shallow and interrupted thick transverse striae and conspicuous longitudinal wrinkles; lower part with 2-3 branch roots. Sun-Dried Whole Fresh Ginseng bears numerous fine long rootlets marked usually with indistinct small verruciform (wart-shaped) protuberances. Rhizome 1-4 cm long, 0.3-1.5 cm in diameter; mostly constricted and curved; with adventitious roots and sparse dented stem scars. Relatively hard. Transverse section pale yellowish-white, starchy; cambium ring brownish-yellow; cortex marked with punctiform (dot-like) yellowish-brown resin ducts and radial clefts. Odour: slightly fragrant and distinctive; taste: slightly bitter, gradually sweet.
Indications
1. General weakness, palpitations, forgetfulness
2. Thirst and hyperhidrosis, anorexia
3. All kinds of chronic disease, posthaemorrhagic shock, collapse
Chemical Composition
Mainly contains triterpene saponins such as ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Rd, Re, Rg1.
Photos